Parkinson Tanısına Yönelik Yeni Optimizasyon Yaklaşımı
Tarih: Date -
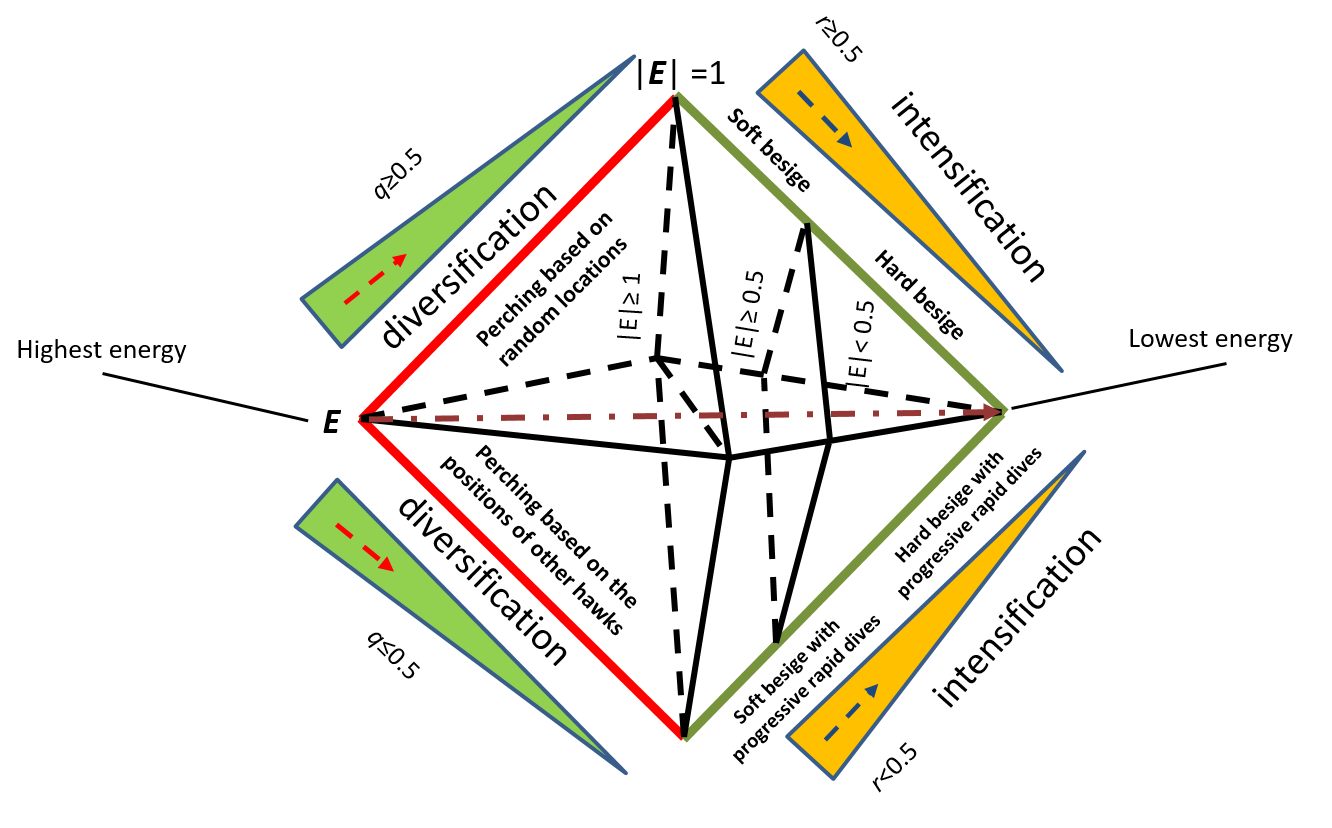
Yazılım Mühendisliği Bölüm Başkanı Prof. Dr. Tansel Dökeroğlu’nun yürütücülüğünü yaptığı yeni çalışma, Parkinson hastalığının bilgisayarlı tanısında özellik seçimini iyileştirmeye yönelik yenilikçi bir yöntem sunuyor. Geliştirilen ikili Çok Amaçlı Harris Hawk Optimizasyonu (MHHO) algoritması, adaptif K-Nearest Neighbor (KNN) sınıflandırıcısıyla birleştirilerek yüksek doğruluk oranları ve verimlilik sağlıyor.
Çalışmada, özellikle büyük veri kümelerinde zaman maliyetini azaltmak amacıyla Message Passing Interface (MPI) tabanlı paralel bir sürüm de geliştirilmiş. MHHO algoritması, mevcut literatürde sık kullanılan Genetik Algoritma, Parçacık Sürü Optimizasyonu ve Cuckoo Search gibi yöntemlerle kapsamlı şekilde karşılaştırılmış ve çoğu veri kümesinde daha başarılı sonuçlar elde etmiştir. Ayrıca, önerilen yöntemle tüm veri kümelerinde %30’un üzerinde özellik azaltımı sağlanarak hesaplama maliyetleri önemli ölçüde düşürülmüştür.
Makalenin özet metni aşağıda yer alıyor:
Parkinson’s disease, an idiopathic neurological illness, affects over 1% of the global elderly population. Feature-based methods are frequently used to diagnose Parkinson’s disease, and selecting the best feature set remains an ongoing and difficult challenge. In this study, we introduce a new binary Multi-objective Harris Hawk Optimization (MHHO) algorithm that combines an adaptive K-Nearest Neighbor (KNN) classifier with novel exploration and exploitation operators for this challenging task. In larger problem instances, where fitness evaluation is a bottleneck, this study proposes a parallel version of the technique that uses Message Passing Interfaces (MPI) to reduce computational complexity. Comprehensive comparisons with state-of-the-art algorithms, including Genetic Algorithm, Particle Swarm Optimization, Binary Bat, Cuckoo Search, and Grey Wolf Optimization, are performed. The results indicate that our proposed algorithms are consistently the most successful in the literature. Furthermore, our analysis provides new optimal solutions that have not previously been reported in the literature. For three of the four well-known datasets, our algorithm outperforms recent studies. Furthermore, the suggested approaches achieve more than 30% reduction in the total number of features across all datasets, thereby significantly lowering computational costs.
Makalenin tam metnine bağlantıya tıklayarak ulaşabilirsiniz: ScienceDirect